Arthritis:
And other rheumatic diseases are frequently associated with old age because
osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, occurs more often among the
elderly. Unfortunately, rheumatic diseases and arthritis can affect people of
all ages.
Below
is a list of some of the types of juvenile arthritis and rheumatic diseases
along with a brief definition of the conditions. We soon will be adding more
information about these conditions to Pain.com.
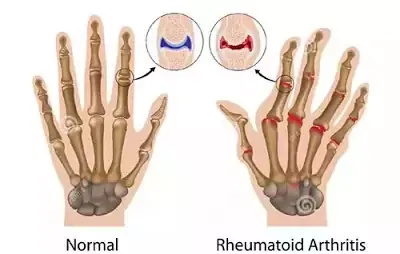
Rheumatoid Arthritis: (JRA)
JRA occurs in children ages 16 or younger. This condition causes inflammation and stiffness of the joints for more than six weeks. Unlike adult rheumatoid arthritis, which is chronic, children often experience periods of remission. However, the disease can affect bone development in the growing child.
Ankylosing Spondylitis:
(JAS) - JAS is a type of arthritis that affects the spine and the
sites where the muscles, tendons, and ligaments are attached to the bone. The
disease causes inflammation of the spine and large joints, resulting in
stiffness and pain.
Psoriatic Arthritis:
This form of arthritis is
associated with psoriasis, which is a chronic skin and nail disease
characterized by red, scaly rashes, and thick, pitted fingernails. The disease
is similar to rheumatoid arthritis in that it involves joint inflammation;
however, psoriatic arthritis affects fewer joints and does not produce the
typical rheumatoid arthritis antibodies.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE):
SLE is a
disease that is characterized by periodic episodes of inflammation of and
damage to the joints, tendons, other connective tissues, and organs, including
the heart, lungs, blood vessels, brain, kidneys, and skin. Often just referred
to as Lupus, it is an autoimmune disorder, which means the body's immune system
attacks its healthy cells and tissues.
Scleroderma:
There are two forms of scleroderma: localized scleroderma and systemic
sclerosis. Localized scleroderma is seen more frequently in children than in the
systemic form. It may involve patches of the skin on the trunk, arms, legs, or
head. Systemic sclerosis is a chronic, degenerative disease that affects the
joints, skin, and internal organs.
Rheumatic Fever:
Rheumatic fever is a delayed autoimmune reaction to the streptococcus
bacteria. It can be prevented with the prompt diagnosis of strep throat and
treatment with antibiotics. It is uncommon in the US, except in children who
have had strep infections that were untreated or inadequately treated.
Rheumatic fever is a complicated, disease that affects the joints, skin, heart,
blood vessels, and brain.
Fibromyalgia:
Although fibromyalgia’s symptoms are similar
to other joint diseases, such as arthritis, it is a form of soft tissue or
muscular rheumatism that causes pain in the muscles and soft tissues. The
actual joints are normal on physical examination.
Source: American College of
Rheumatology!













1 Comments
Nice post and thanks for sharing these different types of arthritis. To treat rheumatology you can also use some natural remedies or visit to doctor.
ReplyDeleteDear Visitors: Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. Thank you!